This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Methadone Clinics
Overview
Introduction
Opioids
Opioids belong to a class of drugs derived from the opium poppy 18. They are a class of drugs derived from the opium poppy seed 2. The drugs are highly addictive and cause a sense of euphoria when taken 2. Opioids are commonly prescribed for their analgesic effects but they can also cause gastric slowing, suppress coughs, and induce euphoria 1,18. They have been historically used for thousands of years. The first records of them being used was by the Ancient Sumerians in 5000 B.C. for religious ceremonies due to the euphoria the user experiences 2. It is unclear exactly when the drug was used as a medication, but it has been used for thousands of years to treat battle wounds and severe traumas 2. Later on, by 8th century A.D. it was spreading all over the world and causing addiction problems 2. Today they are used for their pain relief properties in medicine 2. Popular opioids include morphine which is usually administered pre- and post-surgery to alleviate pain, as well as heroin, fentanyl, and codeine. Rates of opioid abuse and addiction have increased dramatically in the last decade highlighting the need for more therapies to combat the addiction 2.
Opioid Crisis
The opioid crisis has been building up for the last decade and leads to lots of problems in local communities. Recently the increase of the opioid crisis is linked to increase in opioid pain relievers (OPRs) 9. Over prescription leads to addiction, which leads to an increase in overdose and heroin addiction9. From 1999 to 2011, consumption of oxycodone increased 500% and OPR related death has quadrupled9. There is a strong correlation between increases of OPRs and heroin addiction as people switch to heroin once their prescription is finished for pain relief9. From 1997 to 2011, there was a 900% increase in people seeking treatment for opioid addiction9. SAMHSA’s 2014 National Survey on Drug Use and Health estimated that 435,000 people used heroin, accounting for those aged 12 and up9. People in the 18-25 age range were most likely to abuse heroin, although the study reflected an increase in use by adults 26 and older9. Since 2001, overdose deaths for heroin addiction increased 171% and heroin treatment centre admissions have also soared9. A recent study found that physicians prescribed opioids in more than 50% of 1.14 million nonsurgical hospital admissions from 2009 to 2010, often in high doses9. This is a large problem for people since the addiction is hard to recover from once the people are addicted to it.
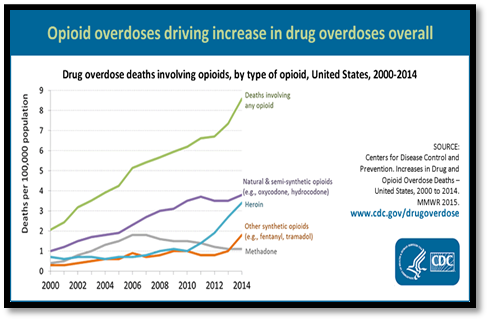
Figure 1: Shows increase of opioid-related deaths over time. https://goo.gl/8KyrX8
History
Methadone clinics were historically opened to be used as an opioid replacement therapy. A German scientist discovered methadone during the 1930s and a substance called polamidon was developed in 1937 19. During World War II there was a morphine shortage, so production was increased 19. In 1947, it was used in the US as a pain relief medicine and subsequently as a narcotic addiction treatment drug 19. As time went on the drug was researched and new regulations were added during the late 19th century 5. Methadone is an effective maintenance therapy. It does not show a statistically significant superior effect on criminal activity or mortality 14.
Opioids and the Brain
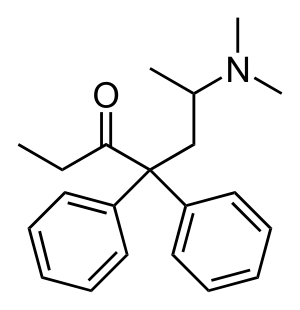
Figure 2: Chemical Structure of Methadone
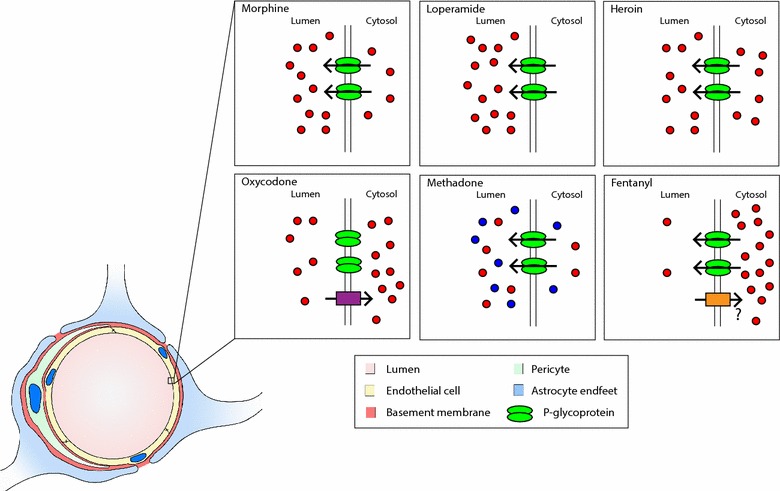
Opioids can be administered intravenously, orally, rectally, or intrathecally (via the spinal cord)1,18. They can have a local effect by acting on nearby nerve receptors, or travel through the blood and reach the brain where they encounter the blood brain barrier (BBB)18. The BBB is a physical and biochemical region that separates the brain’s environment from outside influence such as from chemicals and pathogens. The BBB consists of many regulators and proteins to ensure only certain molecules are allowed to enter. Each opioid has a different rate at which it enters the central nervous system (CNS)3,18. Morphine for example is lipophilic and can therefore cross the membrane of the endothelial cell serving as the physical barrier through passive diffusion. P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is a multiple drug resistant protein that is responsible for the export/efflux of morphine in the brain18. It can act on molecules as they diffuse through the membrane and inside the endothelial cell. Inhibition of P-gp increases the analgesic effect of morphine18.
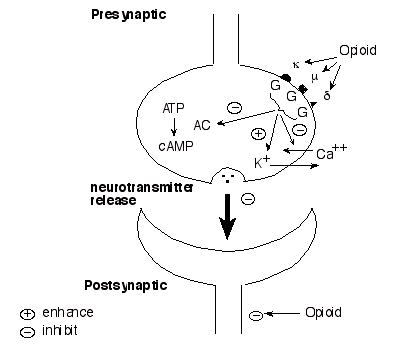
Once inside the BBB and in the interstitial fluid, morphine binds to opioid receptors located on the cell surface. There are three common classes of opioid receptors: mu, delta, and kappa receptors1,3,18. These receptors are coupled with G proteins, a 3 subunit structure (beta, gamma, alpha)3,18. Upon activation of the receptor via binding of morphine, the alpha subunit detaches and forms a complex with an effector resulting in a cellular response3. This response can be initiated on the presynaptic or postsynaptic neuron. The reason for a two pronged response is due to the overall effect of opioids. They produce an inhibitory effect so that an action potential does not arise and the message (pain) is no longer transmitted1,3,18. Because the brain is made up of both excitatory and inhibitory neurons, inhibition of the presynaptic neuron that is inhibitory would produce an excitatory effect, thereby releasing neurotransmitters into the synapse and affect the postsynaptic neuron. By inhibiting the postsynaptic neuron as well, morphine prevents the signal from occurring3.
Opioids inhibit the signal through 3 distinct mechanisms. The receptors are coupled to G proteins as well as voltage gated ion channels1,3. The first mechanism is through inhibition of neurotransmitter release via calcium gated ligand channels which occurs in the presynaptic neuron1,3. Another voltage sensitive ion channel affected are the K+ channels. Opioids open these channels which then increase the rate at which potassium is effluxed from the cell, resulting in hyperpolarization1,3. This means it will take a greater stimulus to initiate an action potential. The last mechanism involves the inhibition of adenylate cyclase1,3. Its normal function is to facilitate the breakdown of ATP to cAMP which is an important factor in neurotransmitter release1,3. Inhibition of this enzyme results in lack of neurotransmitter release.
Opioid addiction occurs very quickly. It has been shown that even after the first injection of morphine, patients can demonstrate withdrawal symptoms18. Receptor antagonists such as naloxone which do not produce any of the inhibitory effects when attached to the receptor, produce severe withdrawal responses3. As a result, most addicts become trapped in a cycle of opioid abuse. The development of methadone provides a more tolerable treatment method for opioid addicts. Methadone is a synthetic opioid that has lesser side effects than traditional opioids3,18. While it consists of R and S enantiomers, there is minimal stereoselectivity. Replacement therapy with methadone involves having addicts switch from harsher opioids to this drug. They can then be gradually weaned off the methadone entirely, with milder withdrawal symptoms, and greater level of success18.
Methadone Clinics
Methadone is used to prevent opioid withdrawal and block the effects of opiate pain medications. Although the treatment must be prescribed by a doctor, it is not a cure for addiction issues 5.
The two main types of clinics are public and private. Public are cheaper and longer waits, private are better equipped. In Canada, free consultation but a cost of $5-15 for the medication each time 5.
Goals of a Methadone Clinic 5:
- Control opioid withdrawal
- Decrease opioid cravings
- Block effects of opioids
- Control behavior so that people can function everyday
There are many methadone clinics throughout the United States. SAMHSA’s 2011 OTP Survey found 245,000 people were apart of an opiate treatment program in 2010 9.
Treatment Types
3 types of Treatment offered 5, 14 :
- Medication-assisted treatment: block the opiate drugs reward pathways to prevent craving and withdrawal.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Counseling to work on coping skills for substance cravings and stress factors that can cause patients to take drugs.
- Medical detox: Withdrawal symptoms are treated so that patients can detox successfully. Usually takes a week, but can last up to a month.
Effectiveness
Reduction In Opioid Usage
The implementation of the methadone maintenance treatment to help addicts reduce the use of heroin is a highly controversial topic with many viewpoints and justifications. Regardless of opposing views, the effectiveness of this treatment cannot be neglected. Considering that methadone maintenance is not a curative method of treatment, but rather a corrective one, evidence shows it to be medically safe and preferred 7. Firstly, this method can be deemed effective with its characteristic of reducing opioid usage. From when the methadone maintenance method was introduced to now, the use of this treatment to cope with opioid dependence has been an area of interest for researchers. A meta-analysis that was published in 1998 by Marsch found a statistically significant correlation between the methadone maintenance treatment and opioid use reduction. Similarly, a more current meta-analysis published in 2007 came to supporting conclusions. Ultimately, a decreasing pattern in opioid dependency can be seen in addicts when the methadone treatment is administered, based on the findings of randomized controlled trials analyzed in these meta-analyses 4. When drawing conclusions about the effectiveness of this treatment, it is important to consider that reductions in opioid abuse depends on whether an appropriate dosage of methadone administered to addicts. Additionally, the maintenance of the reduction depends on the time period that addicts receive methadone. Therefore, it can be concluded that, with proper dosage and consistency of the methadone treatment, addicts are able to overcome their opioid-abusive behaviour15.
Methadone Compared to Other Options
Moreover, studies have found the methadone maintenance treatment to be more effective compared to alternative treatments. In a controlled trial study that compared Buprenorphine and Methadone maintenance in treating opioid dependence, the findings suggested methadone to be more effective than buprenorphine 10. A double-blinded study was conducted with two hundred twenty-five opioid addicts seeking treatment by placing them in one of three groups: 8 mg/d of buprenorphine, 30 mg/d of methadone, or 80 mg/d of methadone maintenance over a one-year timespan. Efficacy was measured by observing both objective and subjective outcomes at middle and end of the study period. These measures included urine toxicology, retention, craving, withdrawal symptoms, and safety data 10. The results of the study suggest that the high dose methadone treatment showed significant improvements in retention, and opioid use and cravings, compared to both the low-dose methadone or buprenorphine groups at both the observational checkpoints of 26-week and 52-week. Ultimately, from the findings of this study it can be concluded that the methadone treatment is more effective compared to alternatives 10. Basically, lower doses of methadone may not be optimally effective or it may even result in the blockade effect. The blockade effect refers to the body’s ability to block the effect of any opiate drug used to treat opioid addiction through cross-tolerance. Essentially, according to multiple studies, the prevalence of illegal heroin usage is significantly higher in addicts receiving low doses of methadone compared to ones receiving higher doses 16.
Cost Effectiveness
The benefits of the methadone maintenance treatment overshadows the costs of administering, especially if the cost of untreated opioid abuse is considered. Ultimately, The cost of imprisonment, drug-free treatment programs,and neglected heroin dependence is significantly higher than that of the methadone maintenance treatment. Specifically, the social costs of illegal opioid usage is four times that of the methadone treatment 15. With regards to cost benefits, Canada is beginning to observe the same trends as the United States– for every dollar spent on methadone maintenance treatment, the community saves between four to thirteen dollars. Specifically, in Toronto, untreated opioid addictions results in an approximate annual cost of $44,600. Contrarily, the estimated cost to provide methadone maintenance treatment in Toronto is $6,00 per year. Ultimately, the methadone maintenance treatment is a cost-effective solution, considering its lower delivery cost and higher retention rates compared to other treatments for opioid addicts 15.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the methadone maintenance treatment shows great promise in solving the opioid crisis. Thus, in order for the methadone maintenance treatment to expand and be more socially acceptable, communities need to overcome the bias and stigma that currently exists. This can be done through increased education and awareness on the treatment and its benefits 19.
References
[1] Akbarali, H. I., & Dewey, W. L. (2017). The gut–brain interaction in opioid tolerance. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 37, 126–130. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2017.10.012
[2] Brownstein, M. J. (1993). A brief history of opiates, opioid peptides, and opioid receptors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 90(12), 5391.
[3] Chahl, A. Loris. (1996) Opioids - mechanisms of action. Australian Prescriber, 19(3), doi: 10.18773/austprescr.1996.063
[4] Connock, M., Juarez-Garcia, A., Jowett, S., Frew, E., Liu, Z., Taylor, R. J., … & Burls, A. (2007). Methadone and buprenorphine for the management of opioid dependence: a systematic review and economic evaluation.
[5] Government of Canada. (2017). Methadone Program. Retrieved from https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/health-concerns/controlled-substances-precursor-chemicals/exemptions/methadone-program.html
[6] Hosseini, S. H., Isapour, A., Tavakoli, M., Taghipour, M., & Rasuli, M. (2013). Erectile dysfunction in methadone maintenance patients: a cross sectional study in northern Iran. Iranian journal of psychiatry, 8(4), 172.
[7] Joseph, H., Stancliff, S., & Langrod, J. (2000). Methadone maintenance treatment (MMT): a review of historical and clinical issues. The Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine, New York, 67(5-6), 347-364.
[8] Kenny, P. J. (2013). The food addiction. Scientific American, 309(3), 44-49.
[9] Kolodny, A., Courtwright, D. T., Hwang, C. S., Kreiner, P., Eadie, J. L., Clark, T. W., & Alexander, G. C. (2015). The prescription opioid and heroin crisis: a public health approach to an epidemic of addiction. Annual review of public health, 36, 559-574.
[10] Ling, W., Wesson, D. R., Charuvastra, C., & Klett, C. J. (1996). A controlled trial comparing buprenorphine and methadone maintenance in opioid dependence. Archives of general psychiatry, 53(5), 401-407.
[11] Lucas, G. M., Mullen, B. A., Weidle, P. J., Hader, S., McCaul, M. E., & Moore, R. D. (2006). Directly administered antiretroviral therapy in methadone clinics is associated with improved HIV treatment outcomes, compared with outcomes among concurrent comparison groups. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 42(11), 1628-1635.
[12] Marden, D. (2016). Western NC Harm Reduction: A Look Inside a Methadone Clinic. Retrieved from https://sobernation.com/western-nc-harm-reduction-a-look-inside/
[13] Marsch, L. A. (1998). The efficacy of methadone maintenance interventions in reducing illicit opiate use, HIV risk behavior and criminality: a meta‐analysis. Addiction, 93(4), 515-532
[14] Mattick, R. P., Breen, C., Kimber, J., & Davoli, M. (2009). Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane database of systematic reviews, (3).
[15] Methadone Treatment Effectiveness. (2018, September 18). Retrieved from https://www.oatc.ca/news-articles-information/methadone-treatment-effectiveness/
[16] Rettig, R. A., & Yarmolinsky, A. (1995). Pharmacology and Medical Aspects of Methadone Treatment.
[17] Stolte, E. (2018). New opiod treatment clinic coming; core communities likely location. Retrieved from https://edmontonjournal.com/news/local-news/new-opioid-treatment-clinic-coming-core-communities-likely-location
[18] Schaefer, C. P., Tome, M. E., & Davis, T. P. (2017). The opioid epidemic: a central role for the blood brain barrier in opioid analgesia and abuse. Fluids and barriers of the CNS, 14(1), 32. doi:10.1186/s12987-017-0080-3
[19] Thorp, R. H., Walton, E., & Ofner, P. (1947). Analgesic activity in compounds related to amidone. Nature, 159(4046), 679.
[20] Towards recovery. (2017). Methadone treatment pros and cons. Retrieved from http://www.towardsrecovery.com/methadone-treatment-pros-cons/
[21] Tran, B. X., Nguyen, L. H., Tran, T. T., & Latkin, C. A. (2018). Social and structural barriers for adherence to methadone maintenance treatment among Vietnamese opioid dependence patients. PloS one, 13(1), e0190941.