This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
DIABETES
Epidemiology
}
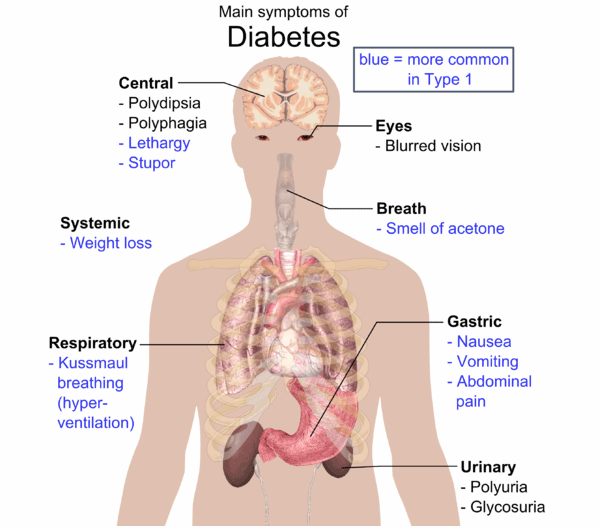
Symptoms
Diagnosis
There are several methods and tests available to screen for diabetes. The most common method is the use of blood tests. A blood test measures high blood glucose levels, which are known to be an indication of diabetes. A total of two abnormal blood tests are required for an official diagnosis for diabetes.
 A1C Test
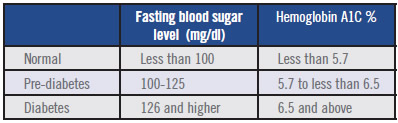
A common blood test that is usually used to screen for diabetes, is the glycated hemoglobin test (A1C). This blood test measures the blood glucose that is attached to hemoglobin. The more there is blood glucose attached to hemoglobin, the higher the level of plasma glucose. In general, an A1C range of 7.5-6.4% indicates prediabetes. And a measure of 6.5% or higher on two A1C tests is an indication of diabetes.
A1C Test
A common blood test that is usually used to screen for diabetes, is the glycated hemoglobin test (A1C). This blood test measures the blood glucose that is attached to hemoglobin. The more there is blood glucose attached to hemoglobin, the higher the level of plasma glucose. In general, an A1C range of 7.5-6.4% indicates prediabetes. And a measure of 6.5% or higher on two A1C tests is an indication of diabetes.
Some patients are not able to get an A1C test done for various reasons , therefore a normal blood glucose test can be done for a diagnosis. A plasma glucose test can be done while fasting or non-fasting (random blood glucose count).
Fasting: - This blood test measures the fasting blood glucose levels. A fasting blood glucose range of 100-125 mg/dL is considered as prediabetes. A result of 126 mg/dL or higher of fasting blood glucose levels is an indication of diabetes.
Non-Fasting: - This blood test measures the blood glucose levels at any random time. A random blood glucose levels of 200 mg/dL or higher suggests diabetes.