Table of Contents
Frequent Users
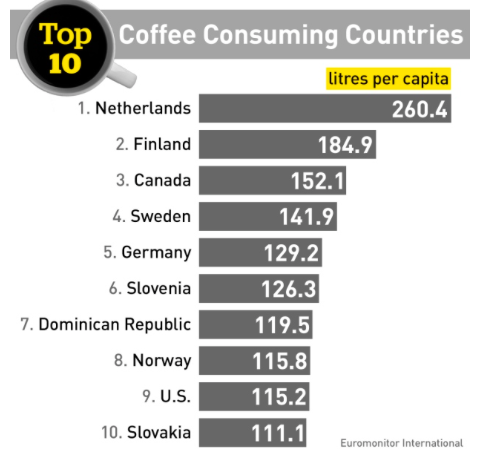
In Canada, on average, individual’s drink approximately 152.1 litres of coffee per person annually (Harris, 2016). However, this does not include other beverages that has caffeine in it, such as tea, soda, and energy drinks. This makes Canada the third country in the world to drink the most coffee (Harris, 2016).
Other data to support this is that Canadians consume 180 mg of caffeine in coffee per day, significantly higher than all but two other countries (Harris, 2016). When considering caffeinated drinks altogether, 73.6% of Canadians aged 12-24 consume a beverage that has caffeine (including coffee, tea, soda, and energy drinks) and 16% of caffeine consumers report exceeding two or more caffeinated drinks per day (Heath, 2016).
Studies have shown that the coffee demand is growing and breaking historical records thanks to millennials of ages 19-34 (Heath, 2016). In the United States, millennials consume 44% of the coffee consumed (Heath, 2016). Those born after 1995 started drinking coffee at about 14.7 years of age, in contrast to those born in the 1980’s that started drinking coffee at 17.1 years of age (Heath, 2016). This could be due to the increase in trend to drink coffee, as it has become a cultural and social activity.
.
General Side Effects
The concentration of caffeine in the blood peaks 30-60 minutes after it is consumed, and has a half life from two to ten hours (Weinberg, & Bealer, 2001). This means that in approximately twelve hours most of the caffeine is diminished from the body (Weinberg, & Bealer, 2001). During that time the caffeine has peaked in the body, medical studies have linked caffeine use to a spectrum of symptoms. Some of which include:
- aggravation
- improving performance of simple tasks, athletic performance
- impairing short term memory
- increasing concentration, insomnia, restlessness, alertness, attentiveness
- suppressing appetite
(Weinberg, & Bealer, 2001)
Specifically, 1 gram of caffeine (equivalent to about six cups of coffee), can induce:
- insomnia
- restlessness
- ringing in the ears
- confusion
- tremors
- cardiac arrhythmias
- vomiting
- diarrhea
(Weinberg, & Bealer, 2001)