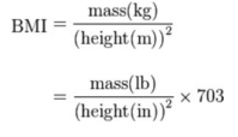This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Obesity
Obesity is a medical disease defined as the excessive accumulation of fat in adipose tissue to the extent that it may harm one’s health. Obesity is one of the leading preventable causes of death worldwide and it is generally diagnosed through the use of the body mass index (BMI) by physicians (Figure 1). <style float-right> </style>
Epidemiology
<style justify>
The prevalence of overweight and obese individuals has increased globally by 37.5% in adults and 41.1% in children between 1980 to 2013. In 1980, there were about 921 million overweight and obese individuals which has grown to 2.1 billion in 2013. [1]
This is particularly true for women, who have consistently shown a higher increase in obesity compared to men. This trend is observed in developing and developed countries alike.The rate of increase of obesity appears to have been greatest between 1992 and 2002, but has slowed down over the last decade, particularly in developed countries.
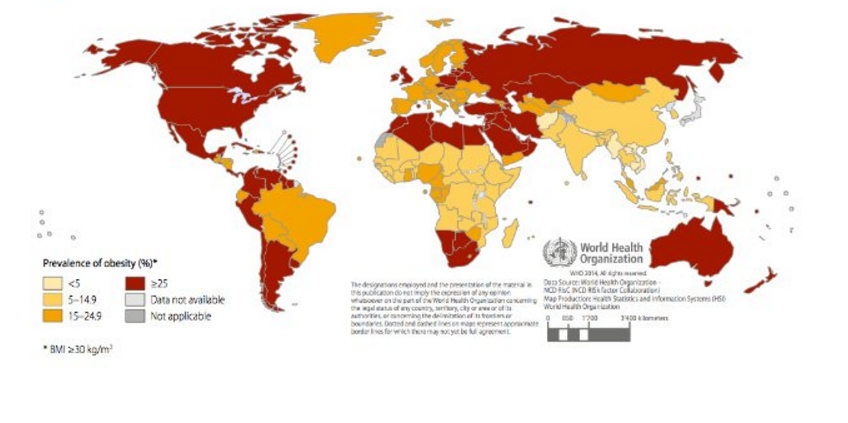
At all ages, prevalence is higher in developed countries (Figure 2). In these countries, men over the age of 15 exhibit higher rates of overweight and obesity than women. In developing countries, women have higher rates than men above age 25. Overweight and obesity peak in developed country men around age 55 years, with 1 in 4 obese. For developed country women, the peak age is closer to 60 years with 31.3% obese.[1]
In 2008, the highest rates of obesity in women were observed, in descending order of severity, in Southern Africa, North Africa and the Middle East, Central Latin America, North America (US and Canada) and Southern Latin America. In men, the top 5 regions were North America (US and Canada), Southern Latin America, Australasia, Central Europe and Central Latin America. Many of these regions consist of low or middle income countries.[2]
The epidemiology of obesity used to be difficult to study because many countries had their own criteria for the classification of obesity. During the 1990s, however, the BMI became a universally accepted measure of body fat, and identical cutoff points are generally recommended. [2]
Diagnosis
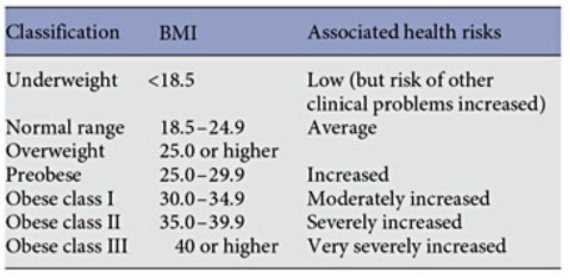
Body Mass Index (BMI)is an index of weight-for-height that is commonly used to classify weight in adults (Figure 3).The BMI was created to estimate the individual’s level of body fat and therefore assesses an individual’s risk of disease.
BMI is measured standardly as weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters (Figure 4). The values of the BMI are age and sex dependent as body composition varies between sexes and at different ages. The values are then assessed by looking at a BMI table or chart.[3]
BMI in children
Obesity is defined differently for children and teens compared to adults due to the fact that they are still growing (Figure 5).
BMIs for this cohort compare their height and weight against growth charts that take age and sex into account, since males and females in this cohort usually mature at different rates.
Their BMI is referred to as BMI-for-age percentile, meaning the child’s BMI is compared with other children of the same sex and age who participated in national surveys that were conducted from 1963-65 to 1988-94.[4]
BMI Limitations
Variance in Asian Populations
There were some debates on whether there is a need for developing different BMI cut-offs for different ethnic groups due to increasing evidence that the associations between BMI, percentage of body fat, and body fat distribution differ across populations and therefore, the health risks increase below the cut-off point of 25 kg/m^2 that defines overweight in the current WHO classification. The WHO Expert Consultation study concluded that the proportion of Asian people with a high risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease is substantial at BMI's lower than the existing WHO cut-off point for overweight, but the cut-off point for observed risk varies in different Asian populations and for high risk. Therefore they concluded that the current WHO BMI cut-off points should be retained as the international classification.[2]
However, overtime, the BMI (weight/height) became a universally accepted measure of the degree of overweight, and now, identical cutoffs are recommended.[2]
BMI in Athletes
Although the BMI is a good gauge of an individual’s level of fat it is problematic in the case of individuals with higher bone and/or muscle mass. Athletes and individuals with jobs that require physical fitness are often wrongly categorized as overweight due to the their muscle mass.[5]
Causes and Risk Factors
<style justify>
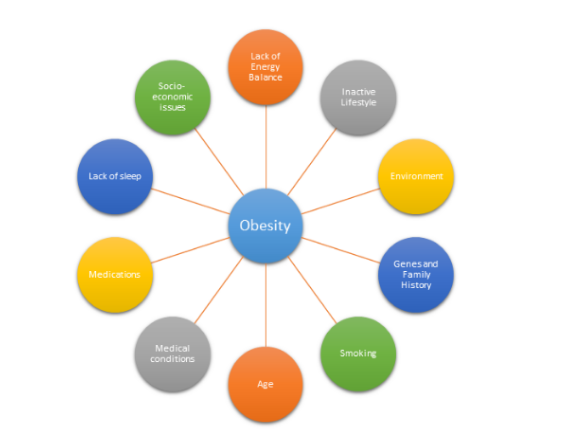
Obesity does not always have a particular cause and effect. There are a plethora of factors that can be associated with obesity and impact the way an individual’s body reacts. The following are:
Energy is Unbalanced
An absence of energy balance is often considered to be the major cause of obesity. Energy balance means that the energy going in, in the terms of calories, equals the individual’s energy out, such as energy that the body uses for things like breathing, digesting, and being physically active. To maintain a healthy weight, the energy needs to be roughly balanced over time [6].
Lack of Active Lifestyle
Generally, developed nations’ citizens are not very physically active. Individuals rely on cars instead of walking, encounter fewer physical tasks at work, or remain at home because of modern technology and conveniences. People who are inactive are more likely to gain weight because they do not burn the calories that they take in from food and drinks. An inactive lifestyle also raises the risk for heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and other diseases [7].
Environment
Sometimes the environment inhibits healthy lifestyle habits and encourages obesity. Some reasons include: lack of neighbourhood sidewalks and safe places for recreation, work schedules are time consuming, oversized food portions, lack of access to healthy foods, and food advertising focused on high-calorie, high-fat snacks and sugary drinks [8].
Genes and Family History
Obesity tends to run in families. The chances of being overweight or obese are greater if 1 or both of the individual’s parents are overweight or obese. Genes also may influence the amount and location of excess fat one stores in their body. Since families usually share food and physical activity habits, there is a link between genes and the environment [9].
Health Conditions
Hormone problems may also cause an individual to become overweight and obese. This includes illnesses such:
Hypothyroidism: A condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. The lack of thyroid hormone slows down the metabolism and causes weight gain [10].
Cushing's syndrome: A condition affecting the body's adrenal glands. The glands make too much of the hormone cortisol which alters nutrient intake. Cushing's syndrome also can develop if a person takes high doses of certain medicines for a long time. Patients have upper-body obesity and fat around the neck with thin extremities [10].
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): A condition that affects about 7% of women of childbearing age. These women often are obese, have excess hair growth, and have reproductive issues along with and other health issues. These problems are caused by high levels of hormones called androgens [10].
Medicines
Certain medicines may cause gain weight. These medicines include specific corticosteroids, antidepressants, and seizure medicines. These pharmaceuticals can slow the rate at which the body burns calories, increases appetite, or causes the body to retain water [11].
Emotional Factors
Some people eat more than usual when they are bored, angry, or stressed. Over time, overeating will lead to weight gain and may cause overweight or obesity [7].
Smoking
It is not uncommon to see people gain weight when they stop smoking. Nicotine raises the rate at which the body burns calories, therefore less calories are burned when one ceases from smoking [12].
Age
As we age, muscle is lost, especially if one is less active. Muscle loss can slow down the rate at which the body burns calories. Midlife weight gain in women is mainly due to aging and lifestyle, but menopause also plays a role. Many women gain about 5 pounds during menopause and have more fat around the waist than before [13].
Pregnancy
Women gain weight to support their child’s development. After giving birth, some women find it hard to lose the weight. This may lead to overweight or obesity, especially after a few pregnancies [14].
Lack of Sleep
Lack of sleep increases the risk of obesity. People who sleep fewer hours also seem to prefer eating foods that are higher in calories and carbohydrates, which can lead to overeating, weight gain, and obesity. Additionally, sleep helps maintain a healthy balance of the hormones that make you feel hungry or full. Sleep also affects how the body reacts to insulin, the hormone that controls your blood glucose level. Lack of sleep results in a higher than normal blood sugar level, which may increase the risk for diabetes [15].
Pathophysiology
Adipocyte Development and Metabolism
<style justify>
</style>
Figure 4: Structure of viral HIV. Retrieved from: https://learner.org/courses/biology/units/hiv/index.html
Hormone Regulation
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the beta cells in the pancreas.[13]They regulate glucose levels by assisting in the use and storage of glucose into muscle, fat, and liver cells. In obese individuals, we see a high incidence of insulin resistance whereby insulin is not able to function in regulating glucose levels. As in normal individuals when one eats, the food breaks down into glucose, and the pancreas secretes insulin. But since the insulin is resistant in obese individuals the glucose absorbance is very low. Since the cells do not have energy, one feels hungry which results in overeating, thus excessive blood glucose and insulin release. This is the way in which obese individuals also become Type 2 diabetic patients. [1]
Adipocytes are one of the most highly insulin-sensitive cell types.2 There are many mechanisms through which insulin is able to promote the accumulation of fat in adipocytes, thus contribute to obesity. Some of which are by promoting the differentiation of preadipocytes to mature adipocytes, transport of glucose, and lipogenesis, while inhibiting lipolysis. [2] Specifically in the liver, insulin resistance is selective in that it stimulates fatty acid synthesis. Therefore, investigating the molecular mechanism underlying insulin resistance is important to understanding the connection between insulin and obesity.
Leptin
Leptin is an appetite-suppressing peptide hormone that is secreted by adipocytes3. In obese individuals, there is a greater mass of adipose tissue, which directly correlates with a greater secretion of leptin. Theoretically, when there is more leptin, individuals should consume less because the hormone is appetite suppressing. However, this is not what happens. In obese individuals, we find that there is a higher appetite-stimulating effect. This contradiction suggests that leptin is not functioning, as it should, hence there is leptin resistance.
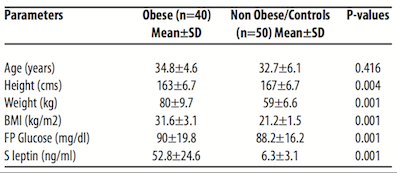
A study conducted by Kazmi et al.(1996) investigated leptin concentrations in a sample of Rawalpindi population. There were three sampling groups—health obese, overweight and non-obese. According to the results as displayed in Figure 1 the mean serum leptin concentration for the obese group was 52.8 ug/mL, and 6.3 ug/mL for the non-obese group. The results of this study concluded there is certainly a positive correlation between the Body Mass Index and leptin concentrations in individuals.4
Figure 5: Results from Leptin Concentration study in Obese and Non-obese individuals. (Kazmi et al. 1996).
Ghrelin
Ghrelin is an appetite-stimulating hormone predominantly secreted by the stomach when it is empty. It increases food intake and promotes fat storage. One would expect the concentration of ghrelin to be higher with obesity because it would account to increased food intake generally involved in cases of obesity. However, this is not the case. Ghrelin concentrations are actually much lower in obese individuals.To investigate the role of ghrelin in obese pathology, Tschop et al. (2001) conducted a study where the plasma ghrelin concentrations of lean and obese individuals were measured. As can be seen in the graph (Figure 2), the plasma ghrelin concentrations of obese individuals are much lower than in lean individuals.5 There seems to be a negative correlation between plasma ghrelin concentrations and fat mass.
This could simply be because of the body’s instinctive shift for homeostasis. Since, ghrelin and leptin both have an antagonistic role, it would not be possible for there to be high concentrations of both hormones. Since, leptin concentration is high it could result in a lowering in ghrelin levels to balance the two hormones.3 The exact mechanism through which this happens is yet to be elucidated by research.
</style>
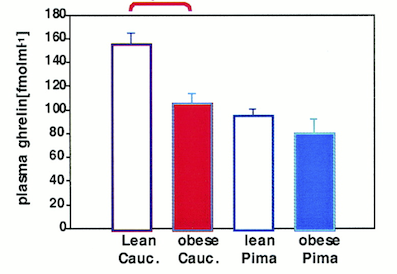 Figure 6: Results of Ghrelin Concentration in Obese and Lean Individuals. (Tshop et al. 2001).
Figure 6: Results of Ghrelin Concentration in Obese and Lean Individuals. (Tshop et al. 2001).
Genetic Predisposition
<style justify>
</style>
Treatments
<style justify>
Goals of Weight Loss and Management
When undergoing weight loss therapy, practice guidelines issued by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute and the North American Association for the Study of Obesity recommend an initial weight loss goal of approximately 10 percent from baseline over a period of 6 months of therapy. (christelle, 1)
Weight loss of 10% has the potential to improve glycemic control, blood pressure control and lipid levels, especially in individuals with type 2 diabetes or hypertension. Additionally, it might help to reduce symptoms from other obesity-related conditions such as gastroesophageal reflex and osteoarthritis. If weight-loss is maintained over a long period of time, adverse clinical outcomes such as myocardial infarction, stroke and cardiovascular-related deaths can be reduced (christelle, 2 )
Intervention For best weight loss and maintenance results, it is important to indefinitely adopt the following lifestyle modifications: dietary therapy, physical activity and cognitive behaviour therapy. Typically, health care practitioners recommend their patients to adopt the lifestyle modifications for 6 months. Thereafter, clinicians assess whether they have reached the weight loss goal of 10% loss from baseline. If patients have reached a satisfactory progress upon evaluation, it is recommended that they maintain their lifestyle modifications for sustainable weight loss results. Regular monitoring is needed. In the case that patients have not reached a satisfactory progress after 6 months, health care practitioners typically recommend pharmacotherapy and/ or bariatric surgery to achieve their weight loss goal. Best results are seen when either pharmacotherapy or bariatric surgery are used in conjunction with lifestyle modifications
Figure 8: HIV Antiretroviral Treatment Retrieved from: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d5/HIV-drug-classes.svg/450px-HIV-drug-classes.svg.png
Diet
Weight Loss Programs
Physical Activity
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
The third component of lifestyle modifications is to undergo a cognitive behaviour therapy (CBT) program to assess one’s current habits and identify factors, stresses or situations which may trigger one’s overeating habits and contribute to one’s obesity. With a CBT approach, patients suffering from obesity can get help through counseling, support groups, as well as adopting the family-based approach (christelle 1,2).
The purpose of the CBT treatment is not to eliminate a psychiatric disorder, but to change eating and exercise behaviours (christelle, 3). This intervention aims to teach skills to change the problematic behaviours. Firstly, CBT is based on a cognitive conceptualisation of the processes that lead to overeating. Specifically, thoughts and thinking patterns are understood as central to the problem. Secondly, CBT is focused on altering the cognitive and behavioural mechanisms that maintain the problem behaviour. Thirdly, CBT uses both cognitive and behavioural techniques to effect change in maintaining mechanisms (christelle, 4). The diagram here shows different components that contribute to CBT.
Counseling is one of the ways a patient can experience CBT. It can either be delivered on a one-on-one basis, or in a group setting of approximately 10 participants with a trained healthcare professional (christelle 5, 6). A study conducted by Renjilian and colleagues comparing the two treatment modalities concluded that participants who were randomized to receive group-based therapy lost more weight after 26 weekly sessions compared to those who were treated individually. Specifically, those receiving group therapy lost about 11 kg after 26 weekly sessions, in comparison to 9 kg for those who were individually treated (christelle, 7).
In addition to counseling, having a support network is important, especially since the individual is undergoing drastic changes. Receiving encouragement from family, friends and health care practitioners can prove to be very motivating during challenging times of the weight loss and maintenance programs. Further, patients can also join support groups with other people undergoing weight loss (christelle, 1).
Lastly, family-based obesity treatment has proven to be a very effective and sustainable approach, especially when treating pediatric obesity. The role of family-based behavioural pediatric obesity treatment is to target eating and activity change in both child and parent. Programs using this approach teach parents behavioural skills to facilitate child behaviour change and mobilize family resources to improve the efficacy of childhood obesity treatments. Simultaneously, treating the child and parent at the same time help to create positive relationships between them, as they both aim to reach their weight loss goal together (christelle 8, 9).
Pharmacotherapy
The Canadian Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management and Prevention of Obesity in Adults and Children recommends that in addition to lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes, physical activity and behaviour therapy, overweight individuals with BMIs greater than 27 kg/m2 but with life threatening diseases, or obese individuals with BMIs greater than 30 kg/m2 can undergo pharmacotherapy (christelle, 2).
A meta analysis investigated 21 randomized control trials (RCT) that involved a total of 11 533 participants using either one of the two drugs: orlistat or sibutramine, or a placebo. These RCTs had a follow-up period of at least 1 year in obese and overweight adults. Olistat functions as a gastrointestinal lipase inhibitor and reduces fat absorption by approximately 30%. Patients can use it for up to two years (christelle, 10). On the other hand, sibutramine functions as a serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor which induces weight loss through enhanced satiety and increased basal energy expenditure. Sibutramine is approved for clinical use for up to 1 year (christelle 11).
Table 14 shows the results from pharmacotherapy trials, which compared the effect of having combined dietary and pharmacotherapy treatment, to dietary treatment only. Patients who received treatment with orlistat or sibutramine, when combined with a reduced-energy diet, underwent a greater weight loss, compared to those who only had a reduced-energy diet. More specifically, the long term weight loss for those receiving combined therapy of dietary and pharmacotherapy was about 6 to 7 kg, compared to about 2 to 3 kg for those who received dietary therapy only (christelle, 2).
Maintenance of weight loss
Studies which assessed orlistat therapy for at least 2 years and up to 5 years showed that weight loss attained by year 1 was better maintained over the subsequent 3 years in patients who received ongoing drug therapy. Specifically, Davidson et al. showed that patients who had ongoing treatment of orlistat for 2 years were associated with less regain of weight loss (32%) compared with diet only therapy (63%) (christelle 12).
In addition, a 2-year study conducted by James et al., showed that 43% of patients who received 6 months of weight loss induction using diet-only therapy, followed by sibutramine-diet therapy had better maintained 80% or more of weight loss, compared to only 16% in the diet-only group who received diet-placebo therapy (christelle 13). This shows that combined therapy is more effective than diet only group.
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery is the treatment method that is considered for adult patients who have a BMI over 35kg/m2 with severe comorbid diseases such as life-threatening cardiopulmonary problems, severe sleep apnea, severe diabetes mellitus, or those in the severely obese category with a BMI greater than 40 kg/m2. As for teenagers, the Canadian Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management and Prevention of Obesity in Adults and Children recommends that bariatric surgery to be limited to an appropriately trained and experienced surgical team. After 6 months of using lifestyle modifications, healthcare practitioners assess the health of the patient and evaluate whether a satisfactory progress of weight loss or goal of 10% of body weight has been reached. In the case that satisfactory progress or goal has not been achieved, physicians will consider the eligibility of patients to undergo bariatric surgery. This is only considered if other nonsurgical weight loss attempts have failed. The goal of bariatric surgery is to relieve a patient suffering from obesity from his or her morbid body weight, improve their comorbidity and improve their quality of life. There are different surgical procedures as shown in the diagram. It is important to note that this treatment option requires lifelong medical surveillance(christelle,2).
A study on obese Swedish patients investigated the conventional, nonsurgical management with surgery for morbid obesity in 2004 found that surgical management is more efficacious than medical management. Patients who received surgical treatment produced greater weight loss, improved lifestyle and dramatic improvement of comorbid disease. At 10 years of follow-up, the surgical cohort showed that they maintained a weight loss greater than 16.1% of their original body weight. In contrast, those who received the conventional, nonsurgical management had a weight gain of 1.6%. This 16.3% weight difference demonstrates the effectiveness and maintenance of surgical procedures (christelle, 14)
References
- A Timeline of HIV/AIDS. (n.d.). Retrieved October 17, 2016, from https://www.aids.gov/hiv-aids-basics/hiv-aids-101/aids-timeline/index.html
- AIDS.gov. (2015). HIV Test Types. Retrieved from https://www.aids.gov/hiv-aids-basics/prevention/hiv-testing/hiv-test-types/AIDS.gov. (2015). HIV Test Types. Retrieved from https://www.aids.gov/hiv-aids-basics/prevention/hiv-testing/hiv-test-types/
- AIDS.gov. (2015). Stages of HIV Infection. Retrieved from https://www.aids.gov/hiv-aids-basics/just-diagnosed-with-hiv-aids/hiv-in-your-body/stages-of-hiv/
- AIDSInfo. (2016). HIV Prevention. Retrieved from https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/education-materials/fact-sheets/20/48/the-basics-of-hiv-prevention
- AidsInfo. N.d. HIV Life Cycle. Retrieved from: https://aidsinfo.nih.gov/education-materials/fact-sheets/19/45/hiv-aids--the-basics
- Berger, E., Garrett, L., MacGregor, R. R., Vonmuller, E., Weiner, D. 2016. HIV and AIDS. Annenberg Learner. 91-106.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2016). HIV/AIDS Testing. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/basics/testing.html
- Global HIV/AIDS Overview. (2016, September 28). Retrieved October 20, 2016, from https://www.aids.gov/federal-resources/around-the-world/global-aids-overview/index.html
- Hall, H., Geduld, J., Boulos, D., Rhodes, P., An, Q., & Mastro, T. et al. (2009). Epidemiology of HIV in the United States and Canada: Current Status and Ongoing Challenges. JAIDS Journal Of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes, 51(Supplement 1), S13-S20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/qai.0b013e3181a2639e
- Holland, K., & Krucik, G. (2013, July 12). The History of HIV. Retrieved October 17, 2016, from http://www.healthline.com/health/hiv-aids/history#EarliestCase1
- Large-Scale HIV Vaccine Trial to Launch in South Africa | NIH: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. (2016, May 18). Retrieved November 04, 2016, from https://www.niaid.nih.gov/news-events/large-scale-hiv-vaccine-trial-launch-south-africa
- Nordqvist, C. (2016, May 11). “HIV/AIDS: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments.” Medical News Today. Retrieved 26 October 2016, from http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/17131.php.
- Robinson, J. (2016). Understanding Treatment of AIDS/HIV. WebMD. Retrieved 26 October 2016, from http://www.webmd.com/hiv-aids/guide/understanding-aids-hiv-treatment?page=3
- Sharp, P. M., & Hahn, B. H. (2011). Origins of HIV and the AIDS pandemic. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine, 1(1), a006841.
- Simon, V., Ho, D. D., Karim, Q. A. 2006. HIV/AIDS Epidemiology, pathogenesis, prevention and treatment. The Lancet, 368: 489-504.
- Surugue, L. (2016, November 2). First large-scale HIV vaccine trial in seven years to start in South Africa. International Business Times. Retrieved November 2, 2016, from http://www.ibtimes.co.uk/first-large-scale-hiv-vaccine-clinical-trial-seven-years-start-south-africa-1589468
- University of California San Francisco. (2006). HIV Antibody Assays. Retrieved from http://hivinsite.ucsf.edu/InSite.jsp?page=kb-02-02-01